Alongside the writings of Trito-Isaiah, there are a further two prophets whom we can date to the specific time soon after the exiles had returned to Jerusalem. The books of Haggai and Zechariah each open with a specific date, both placing their activity in the time of Darius, King of Persia. Malachi is not dated, but is generally considered to have been written fairly soon after Haggai and Zechariah. (The remaining “minor prophets”, Jonah and Joel, however, contain no such indication as to their date.)
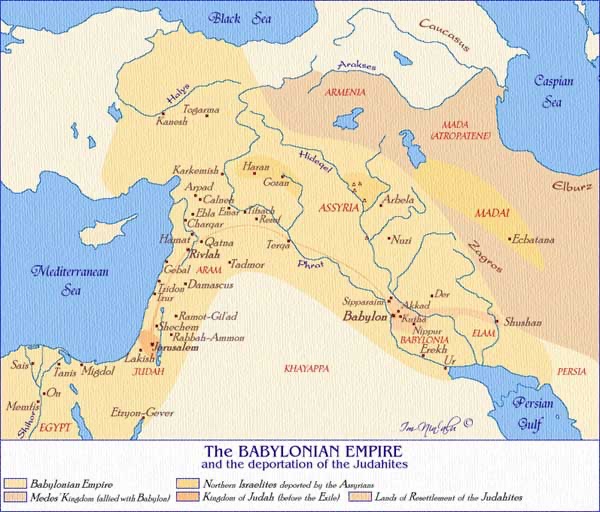
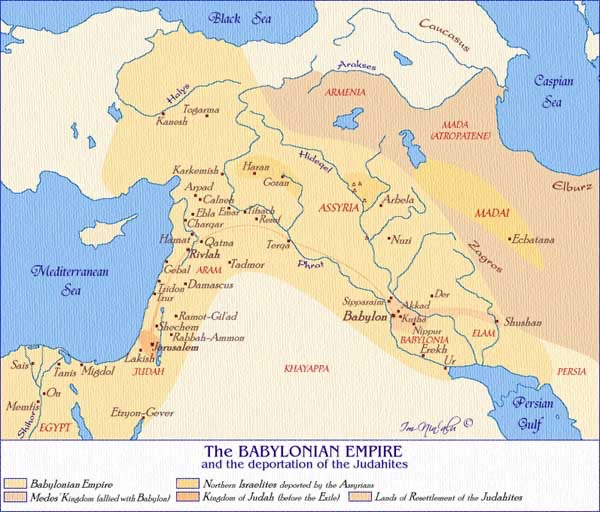
Haggai and Zechariah are located in the period when the exiles in Babylon are returned to Judah late in the 6th century BCE, by decision of the Persian King, Cyrus (whom Deutero-Isaiah, you may remember, described as God’s “Messiah”). In his decree, Cyrus acknowledges “the Lord, the God of heaven” and states that “any of those among you who are of his people … are now permitted to go up to Jerusalem in Judah, and rebuild the house of the Lord, the God of Israel” (Ezra 1:2–4).
Under Nehemiah as Governor, worship is reinstituted in Jerusalem (Ezra 3:1–7), the walls around the city of Jerusalem are rebuilt (Neh 2—6, 12), and the Temple is rebuilt and rededicated (Ezra 5–6). After this, the Law is read in the city under the guidance of Ezra, a priest who is also described as a scribe (Neh 8) and the covenant with the Lord is renewed (Neh 9–10).
Initially, there was opposition to the rebuilding works from “the enemies of Judah and Benjamin” (Ezra 4:1–16), and with intervention from King Artaxerxes, work on the temple ceased (Ezra 4:17–24). The narrative in Ezra reports that “the prophets, Haggai and Zechariah son of Iddo, prophesied to the Jews who were in Judah and Jerusalem, in the name of the God of Israel who was over them” (Ezra 5:1), and work on restoring the temple recommenced (Ezra 5:2).
Further opposition emerged (Ezra 5:3–17), resulting in intervention from King Darius that decreed “let the house be rebuilt … let the Governor of the Jews and the elders of the Jews rebuild this house of God on its site … let it be done with all diligence” (Ezra 6:1–12).
The end result is that the prophets of the Lord and the rulers of the Persian Empire together ensure that the temple is restored: “So the elders of the Jews built and prospered, through the prophesying of the prophet Haggai and Zechariah son of Iddo. They finished their building by command of the God of Israel and by decree of Cyrus, Darius, and King Artaxerxes of Persia” (Ezra 6:14).
*****
What is it, then, that Haggai and Zechariah say to the people? The prophetic words of Haggai are nestled within a relatively brief narrative telling of this return to Jerusalem; they were delivered over a short period of time from “the second year of King Darius, in the sixth month, on the first day of the month” (Hag 1:1) until “the twenty-fourth day of the ninth month, in the second year of Darius” (Hag 2:10, 20).
In the course of those three months, Haggai condemns the people for failing to rebuild the ruined temple while people live in “paneled houses” (1:4), encourages the people to “go up to the hills and bring wood and build the house” (1:8), and then declares that “the latter splendor of this house shall be greater than the former, says the LORD of hosts; and in this place I will give prosperity, says the Lord of hosts” (2:9).
Haggai then relays an ominous word of the Lord: “I am about to shake the heavens and the earth, and to overthrow the throne of kingdoms; I am about to destroy the strength of the kingdoms of the nations, and overthrow the chariots and their riders; and the horses and their riders shall fall, every one by the sword of a comrade” (2:21–22). Yet this short book ends with a positive note for the future, promising to make Zerubbabel, who led the first wave of exiles to return to Judah, “like a signet ring, for I have chosen you” (2:23).
(An excerpt from Haggai appears in the lectionary on the 22nd Sunday after Pentecost.)
*****
Zechariah dates his opening prophecy to “the eighth month, in the second year of Darius” (Zech 1:1), which places him as a contemporary of Haggai. Zechariah begins witha familiar prophetic refrain: “return to me, says the Lord of hosts, and I will return to you, says the Lord of hosts” (1:3), noting that when this message was presented to earlier Israelites, “they repented and said, ‘the Lord of hosts has dealt with us according to our ways and deeds, just as he planned to do’” (1:6).
What follows this opening salvo is a report of eight visions (1:7—6:8). They are dated to “the twenty-fourth day of the eleventh month, the month of Shebat, in the second year of Darius” (2:7), two months after the final prophecy of Haggai. The visions combine glimpses of hope with reminders of the need to remain faithful to the covenant: “if you will walk in my ways and keep my requirements, then you shall rule my house and have charge of my courts” (3:7). The fourth vision (3:1–10) includes the figure of “the accuser” (ha-satan in Hebrew) standing at the right hand of Joshua, to accuse him (3:1).
At the conclusion of the eighth vision there follows words of condemnation (7:1–7) and punishment (7:8–14), citing classic prophetic notes: “render true judgments, show kindness and mercy to one another; do not oppress the widow, the orphan, the alien, or the poor; and do not devise evil in your hearts against one another” (7:9–10).
Then come words of promise (8:1–23): “I will return to Zion, and will dwell in the midst of Jerusalem; Jerusalem shall be called the faithful city, and the mountain of the Lord of hosts shall be called the holy mountain” (8:3). Once again, prophetic injections are offered: “speak the truth to one another, render in your gates judgments that are true and make for peace, do not devise evil in your hearts against one another, and love no false oath” (8:16–17).
An oracle pronouncing judgement on other nations then follows (9:1–8), followed by a joyful celebration of the restoration of Judah (9:9–11:3), introduced by a rousing shout of joy: “rejoice greatly, O daughter Zion! Shout aloud, O daughter Jerusalem! Lo, your king comes to you; triumphant and victorious is he, humble and riding on a donkey, on a colt, the foal of a donkey.” (Zech 9:9). This verse is well-known, of course, from its quotation in the story of Jesus’s entry into the city of Jerusalem (Matt 21:5).
The remaining chapters continue the note of exultation about the future, reworking the motif of “the day of the Lord” so that it signals joy for Jerusalem and terror for other nations (12:3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 11; 13:1, 2, 4; 14:1, 4, 6, 8, 9, 13, 20, 21). A triumphant note of universalism is sounded: “on that day “the Lord will become king over all the earth” (14:9) and “all who survive of the nations that have come against Jerusalem shall go up year after year to worship the King, the Lord of hosts, and to keep the festival of booths” (14:16).
*****
See also