Each year during the Sundays which follow after the festival of Pentecost, the Gospel readings offer a series of stories, encounters, and parables from the Gosepl attributed to Matthew. In parallel to those stories, in the Hebrew Scripture readings, the lectionary offers a sequence of passages telling some of the key moments in the story of Israel, from the narrative books, Genesis, Exodus, Deuteronomy, Joshua, and Judges. These stories run through until the Twenty-Fifth Sunday after Pentecost, in mid-November.
This sequence of passages offers us stories which were told, retold, and probably developed over quite some time by the elders in ancient Israel. They are stories which define the nature of the people and convey key values which were important in ancient Israel. These faithful people from the past stand, for us today, as role models to encourage us, centuries later, in our own journey of faith. They are stories which are worth holding up for our reflection and consideration.
These stories each have the function of an aetiology—that is, a mythic story which is told to explain the origins of something that is important in the time of the storyteller. The online Oxford Classical Dictionary defines an aetiology as “an explanation, normally in narrative form (hence ‘aetiological myth’), of a practice, epithet, monument, or similar.”
Whilst telling of something that is presented as happening long back in the past, the focus is on present experiences and realities, for “such explanations elucidate something known in the contemporary world by reference to an event in the mythical past”.
The ancestral narratives of Israel (Gen 12–50), as well as the series of books known as “the historical narratives” (Exodus to 2 Kings, Ezra—Nehemiah) are all written at a time much later that the presumed events which they narrate. The final form of the books as we have them most likely date to the Exile or post-exilic times, although pre-existing sources would have been used for many of these stories. (There are specific references to earlier written documents—now lost to us—scattered throughout 1—2 Kings.)
Those older stories were remembered, retold, and then written down, because they spoke into the present experiences of the writers. Common scholarly belief is that the stories found in Gen 12–50 were originally oral tales, that were collected together, told and retold over the years, and ultimately written down in one scroll, that we today call Genesis.
*****

For this coming Sunday (the Second Sunday after Pentecost), we are offered the account of the calling of Abram, who journeys into a new future (Gen 12:1–9). This has been a key passage for Jews throughout the centuries; Abram is remembered and honoured as “the father of the nation”—indeed, as “the father of all nations”; and this passage claims that it was God’s intention to grant the blessing of abundant descendants to Abram and his wife, to fulfil this promise.
The passage is found after the opening 11 chapters, which are often labelled the “Primeval History”, since they recount the creation of the world and the sequence of events which were fundamental for understanding human existence (such as human sinfulness and conflict, the expansion of humanity, the great flood, the growth of tribal entities, and the diversification of languages).
The passage also stands at the head of those stories, originally oral, which were collected because they revealed much about the nature of Israel as a people and as a nation. These chapters tell stories about the patriarchs and their wives (Abram and Sarai, Isaac and Rebekah, Jacob and Leah and Rachel). This particular passage introduces key themes for the people of Israel.

The passage indicates that Abram took his wife Sarai and his nephew Lot with him, “and all the possessions that they had gathered, and the persons whom they had acquired in Haran; and they set forth to go to the land of Canaan” (Gen 12:5). They would also have had the (always unnamed) wife of Lot with them, for their companions would undoubtedly have included both males and females within the extended family grouping. We need to read this ancient aetiology with a contemporary critical awareness. Certainly, the faith of Abram and Sarai and their extended family is a key message conveyed by this passage.
The story explains four important aspects of life and faith for the people of ancient Israel and on into contemporary Judaism: the land is given to this people, the people (of Israel) will become “a great nation”, the name (of Abram) will be blessed, and the descendants of Abram, “all the families of the earth”, will likewise be blessed. These four points—land, pepople, name, descendants—loom large throughout the history of Israel. Indeed, they maintain their potency into the present age—and need to be read and understood with political and cultural sensitivity today.
*****
This passage sounds the initial claim of the people of Israel to the land of Canaan. This was promised by God to Abram and his descendants, we are told. They set out towards that land; “when they had come to the land of Canaan, Abram passed through the land to the place at Shechem, to the oak of Moreh. At that time the Canaanites were in the land. Then the Lord appeared to Abram, and said, ‘To your offspring I will give this land.’ So he built there an altar to the Lord, who had appeared to him.” (Gen 12:5–7). The claim recurs at various points throughout the ensuing narratives, culminating in the conquest narrated in the book of Joshua.
See more on this aspect of the passage at
and on the difficulties involved in the story of invasion and violent colonisation, see
In his commentary on this passage in With Love to the World, the Revd Dr John Jegasothy, a retired Uniting Church Minister originally from Sri Lanka, reflects on this story of journeying to a new land, from his own perspective as an asylum seeker some decades ago. “As a family we had to decide to leave Sri Lanka and migrate to Australia on Special Humanitarian Visa as I was a human rights advocate and death came close. God had a plan for me to be an advocate for refugees here.”
Dr Jegasothy continues, “I look at our journey as a journey like Abram and Sarai undertook. They absolutely trusted in God’s promises and because of their faith they were counted as righteous.” There is an invitation here for each of us to ponder this story, in terms of our own journey of faith. How and when has God called us on to journey into new places or new experiences?
*****
Alongside the claim to the land of Canaan, the story of Gen 12 portrays Abram (and Sarai) as the origin of a multitude of descendants; through them, “all the families of the earth shall be blessed” (12:3). Initially, this claim appears to be quite precarious; after all, the first mention of Sarai indicates that “Sarai was barren; she had no child” (11:29–30).
Later, when Sarai advises Abram, “see that the Lord has prevented me from bearing children; go in to my slave-girl; it may be that I shall obtain children by her” (16:1–2), Abram diligently obeys; he “went in to Hagar, and she conceived; and when she saw that she had conceived, she looked with contempt on her mistress” (16:4). Tensions between the wife, Sarai, and the slave-girl, Hagar, lead to Hager’s flight into the wilderness, where she gave birth to Abram’s son, Ishmael (16:7–16).
Still later, when Abram (now Abraham) sealed the covenant with the Lord God through the ritual of circumcision (17:1–14), he is told that Sarai (now Sarah) will now be blessed by the Lord, for “I will give you a son by her; I will bless her, she shall give rise to nations; kings of peoples shall come from her” (17:16). And in due time—despite the laughter of Sarah (18:12)—Isaac is born (21:1–3).
The lectionary studiously avoids the story of the birth of Ishmael, but provides us with a sequence of passages that recount the promise to Sarah (18:1–15, Pentecost 3A), the banishing of Hagar and Ishmael (21:8–21, Pentecost 4A), and the near-sacrifice of Isaac (22:1–14, Pentecost 5A), before turning to the story of Isaac and his wife Rebekah (Pentecost 6A) and then on to Jacob (with excerpts from chs. 25 to 37, Pentecost 7A to 11A).
After Sarah died, Abraham married Keturah and had six sons with her (25:1–4). He also “gave gifts to the sons of his concubines while he was living” (25:6), so there were other (unnamed) progeny of Abraham. In due time, Abraham and Sarah’s son Isaac and his wife Rebekah gave birth to twins, Jacob and Esau (25:19–26), whilst Ishmael, the son of Abraham and Hagar, was the father of twelve sons who had many descendants (25:12–18), as well as a daughter who was the ancestor of the Edomites. Abraham’s brothers Nahor fathered twelve sons (22:20–24) whilst Haran was the father of Lot (11:27), who himself fathered Moab and Ammon. Many of these descendants continued reproducing, and so the line of Abraham grew and expanded, generation by generation.
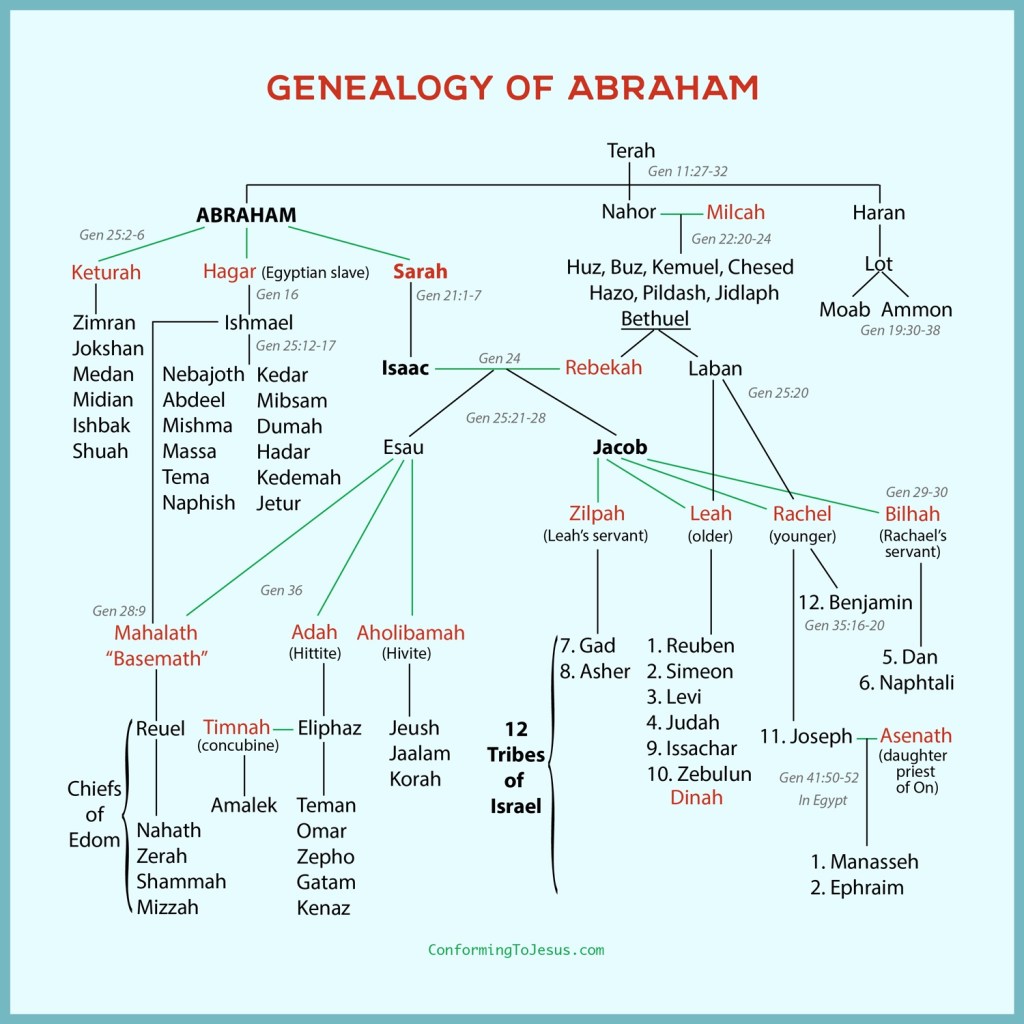
Collectively, this family was responsible for a multitude of descendants, which brings to fulfilment God’s promise to Abraham, “I have made you the ancestor of a multitude of nations; I will make you exceedingly fruitful; and I will make nations of you, and kings shall come from you” (17:5–6). The tenuous moments in the story leave us, as readers, wondering whether this promise would come to fruition; in time, of course, that fulfilment is reported in the Genesis narrative. Abraham does indeed become “father of all nations”, and a key figure in the sagas about Israel that were told and retold throughout the ages.




