Last week, as the lectionary invited us to hear the closing section of Deuteronomy, we turned our attention to the land that was promised to Moses and the people of Israel. Land, as we know, can be contentious. Land claims often ferment into conflict. Acceptance—or rejection—of First Peoples’ Connection to Country in Australia underlies the current political situation downunder. And contested claims to land in the Middle East, from millennia ago, undergird the current disastrous situation that is unfolding there.
The Hebrew Scripture passage for this coming Sunday, from Joshua 3, continues the focus on land. It tells a part of the larger story of the Conquest of Canaan; the taking of the land by force. This story of the Hebrews entering the land of Canaan, battling the inhabitants and colonising the territory, lies underneath the whole story of Exodus, wilderness, and conquest, which is at the heart of the biblical narrative that accounts for the origins of Israel as a nation.
The story of invasion and conquest is told in all its bloody detail in the book of Joshua. Perhaps because of this, the lectionary offers us very few passages from this book in the three years of the lectionary—and one such occasion occurs this coming Sunday (Pentecost 23A), when we are invited to hear Joshua 3:7–17. There are a number of factors to consider when reading or hearing this passage, or any passage in the book of Joshua, and indeed any section of this long, extended saga of the origins of Israel.
Joshua as history?
The story from Joshua tells, in a highly stylised way, of the entry of the people of God into the promised land. This is a key moment in the extended narrative that stretches from Genesis to 1 Kings, recounting stories of the ancestors, a time of slavery in Egypt, the redemptive moment of Exodus, the giving of the Law, the long haul of wilderness wanderings, the battles waged to capture the land under the Judges, and the ultimate vindication of the establishment of the kingdom of Israel under King David.
Of course, it didn’t actually happen like this. For one thing, the book of Joshua is almost universally considered to be a wonderfully embellished and highly stylised narrative constructed by the priests in the sixth century BCE, as they prepared to lead the exiled people of Israel in their return to the land from which they had been removed. So it is an account from many centuries after the events that it purportedly recounts.
The book as a whole is marked by the schematic structuring that was so characteristic of priestly narratives. Structure and order was central to the priestly mindset and is evident in their literary style. We might note how Gen 1:1—2:3 is carefully structured, and observe the structure of the whole book of Numbers, as well as the whole book of Joshua; and we can also note the repeated formulaic assessment of various kings in 1 Ki 11:6, 11:19, 14:22, 15:5, 15:11, 15:26, 15:34, 16:7, etc.
For another thing, we know that the division of Israel into the twelve tribes (3:12), so important in the story that the priests of Israel tell about the nation, was a later ideological construction of the priestly story-tellers. As far as we know, there were no neatly schematised tribes at the time of this incident.
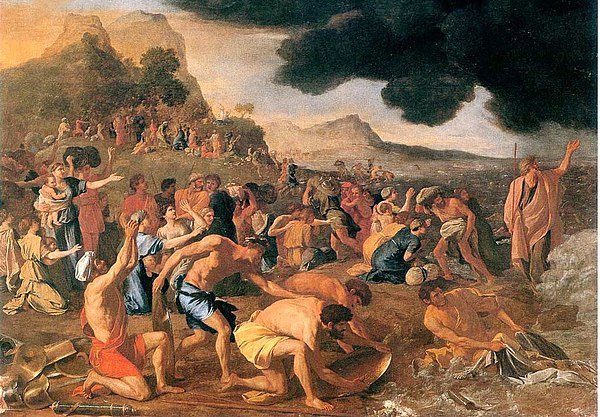
And, of course, the whole story of Exodus, liberation, wilderness and conquest, is beset by multiple historical problems. There is no evidence in the records of the Egyptians about the escape of a large crowd of slaves, not any record of the destruction of the Egyptian Army in the Red Sea. There are no remains in the wilderness between Egypt and Israel that suggest that such a large crowd was travelling, for many years, through the desert—no remains of campsites, no graves of deceased people have ever been found. And there is no archaeological evidence that correlates with the biblical record of the capture of Jericho and other cities in the land. All we have is the story told in the Bible.
The form of the story we have was written down quite some centuries from when the event is alleged to have taken place. It serves an ideological purpose, as the exiled people prepare to return to the land. As the 5th century exiles enter the land, the story of the wandering tribes entering the land from centuries before provides encouragement and inspiration.
So it is not the historical reliability of this incident itself that is to the fore as the story is told. What we, in the post-Enlightenment era, understand to be “history”, is very different from the way that “history” was understood in the time when the story was written.
Joshua as saga
Rather than history, the narrative offers us a saga that invites us into a creative, thoughtful pondering of the story. It offers the people of Israel, exiles returning from Babylon, hope and assurance for their future. The best question we can ask of this story, is not, “did this actually happen?”, but rather, “what does this story offer to us, today?”
Central in the story is the ark of the covenant. The story tells of the time at Mount Sinai when God established a covenant with Moses and Israel, and the giving of the Law within that covenant relationship. The ark is a sign of the presence of God, continuing on with the people of Israel beyond Mount Sinai (Exod 25:10–22). God is not an absentee God, but very present amongst the people. The ark symbolises and reinforces that message.
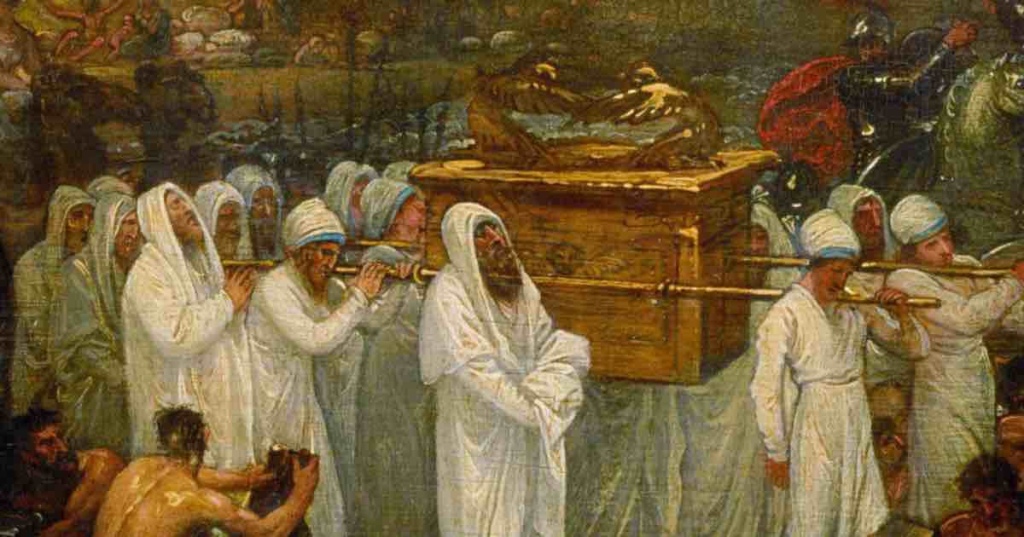

The priests serve to mediate the presence of God. They carry the ark of the covenant, maintaining it, ensuring that it remains safe (Deut 10:8; 31:9, 25–26; Josh 3:3, 6, 8, 13). The story offers an indication that holy people are necessities in life; their mediation of the divine in the midst of the mundane is important. (As an ordained person, I confess that I have a vested interest in this claim!) As the priests shape the story, they make sure that priests play a central role in what is narrated.
Joshua as testimony to faith
The story contains a memorable description of God as “the living God” (3:10). The phrase appears elsewhere in a Hebrew Scriptures (Deut 5:26, 1 Sam 17:26, 36, 2 Kings 19:4, 16, Ps 42:2, 84:2, Isa 37:4,17, Jer 10:10, 23:36, Dan 6:20, 26, Hos 1:10) and also in the New Testament (Matt 16:16, 26:63, Acts 14:15, Rom 9:26, 2 Cor 3:3, 6:16, 1 Thess 1:9, 1 Tim 3:15, 4:10, Heb 3:13, 4:12, 9:14, 10:31, 12:22, Rev 7:2). The ark is a sign that this living God is present, active and engaged in the lives of the people.
A striking event demonstrates this: as the priests stand in the river, the waters stand still (3:16), and so the people are able to cross the river and enter the land. Of course, later on in Joshua, another miraculous event takes place, as the sun stands still (10:13). These were not actual events, but symbolic of divine intervention. The waters standing still evokes the moment in the Exodus story when the waters of the Sea of Reeds parted to allow the Israelites to pass through (Exod 14:21–22, 29).

We might well compare the New Testament story of the earthquake and resurrection of the saints (found only in Matt 27) after the resurrection of Jesus. This, too, was not an historical event; it was a dramatic tale told to underline that God was active in the story.
The key aspect of the story of the escape from Egypt, as the story is found in Exodus 14—15, is the connection with the Feast of the Passover. The story that is attached to the Exodus actually serves a liturgical purpose; the priests have developed the story to reinforce and highlight the way that God was able to redeem the people—as in the story, so in the experience of the returning exiles.
Likewise, the key aspect of this story of the entry into the land, in Joshua 3, is not the actual physical wading across the river, but the assurance of faith that comes from the telling of the story of entering the land. God is not only the redeemer, who delivers the people into freedom, but the one who delivers the land to the people. The promise of the gift of land, first made to Abraham (Gen 12:1, 15:7, 17:8), then reiterated to Jacob (Gen 28:4,13, 35:12) and again to Moses (Exod 3:8,17, 6:4,8, 12:25, 13:5,11), is now coming to fulfilment.
Joshua as military victory
Indeed, the crossing of the river itself points to the symbolism that this story contributes to the overarching narrative. Leaving Egypt, the Lord God parts the waters, the people pass through, the army is bogged and drowned, and their escape from Egypt is secure. Entering Canaan, the Lord God once again stops the flow of the waters, the priests who carried the ark of the covenant enable the people to cross the river and enter the land, and their hold on the land is made secure. Josh 4:19–24 draws this comparison quite explicitly.
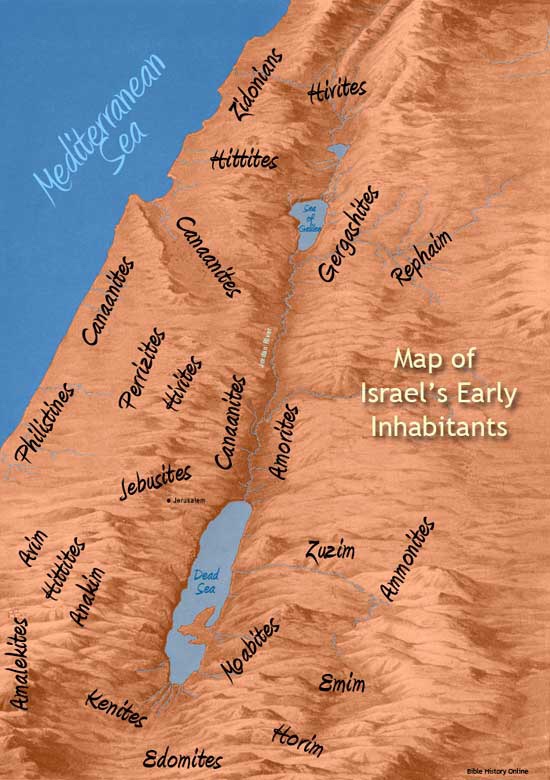
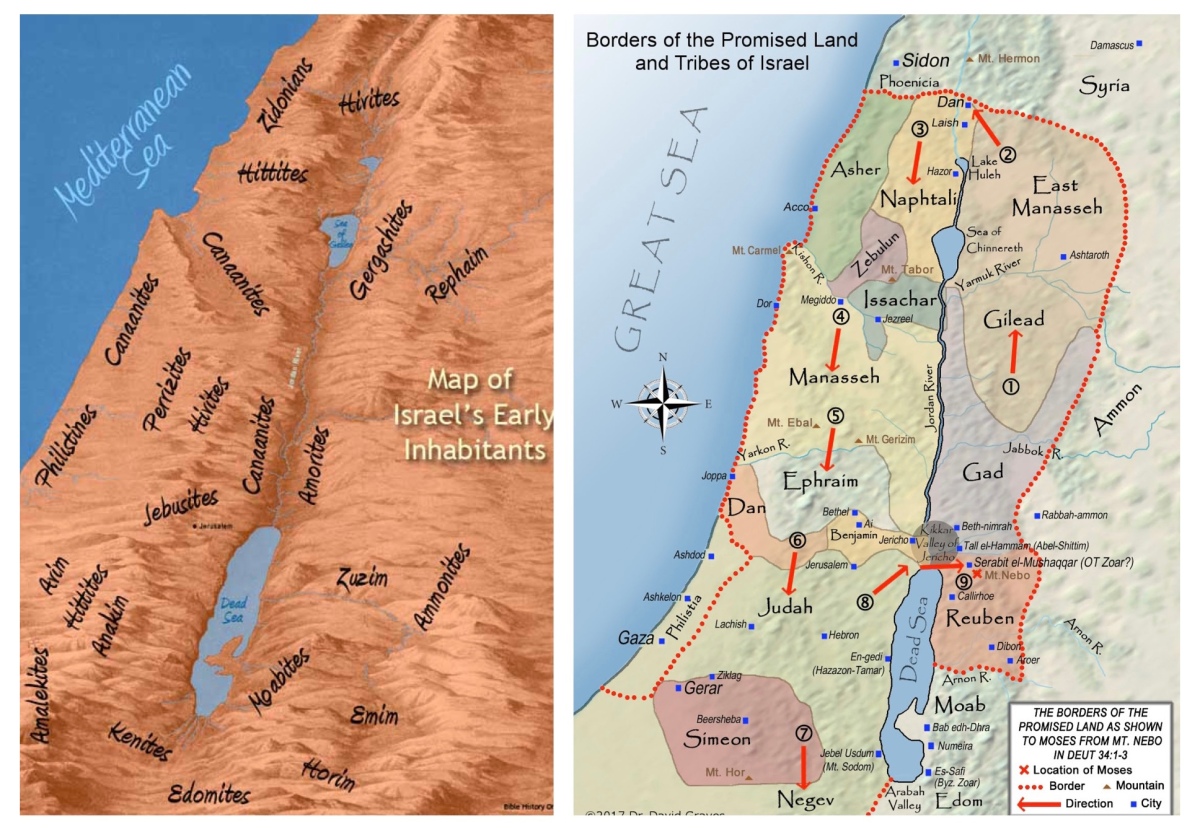
The parallel continues in the strong militaristic element, found in the list of the peoples whom “the living God who without fail will drive out from before you”. The text specifies “the Canaanites, Hittites, Hivites, Perizzites, Girgashites, Amorites, and Jebusites” (3:10). Even before the battles are waged, the victories have been declared. This also provides a neat bookend: the army of Egypt is crushed in Exodus 15, the inhabitants of the land are subdued and defeated in Joshua 3.
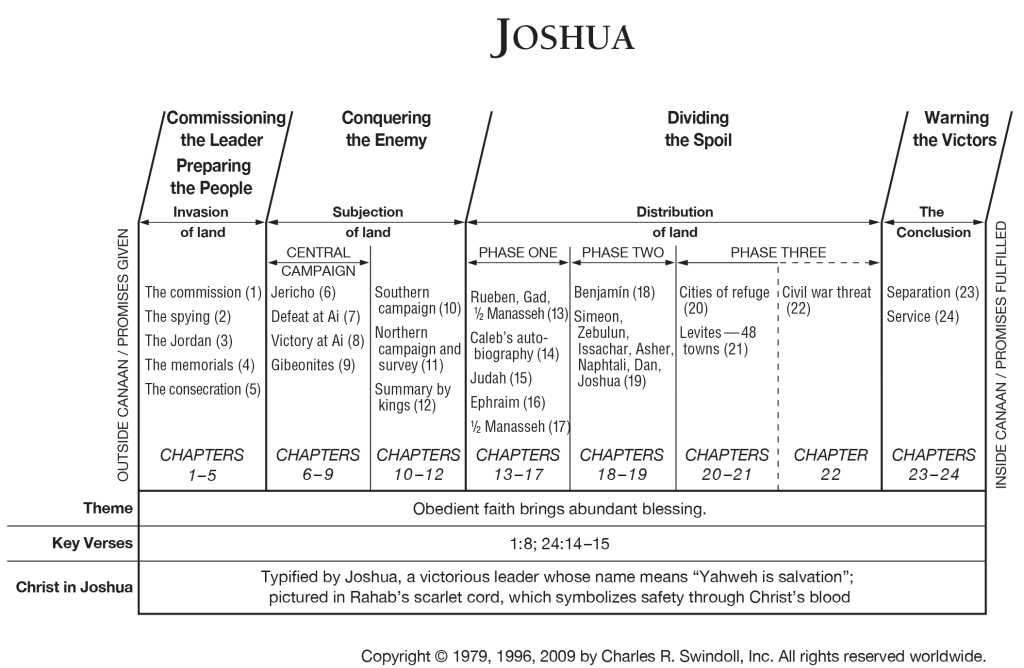
What follows on from this story of entering the land is a highly schematic presentation of the military conquest of the land, in the rest of the book of Joshua. The invaders take the key areas in turn: first the Central area (chs. 6—8), then the Southern regions (chs. 9—10) followed by the Northern areas (ch 11). Chapter 12 then provides a summary of the conquest, listing “the kings of the lands whom the Israelites defeated”—a kind of victor’s gloating, “thirty-one kings in all” (Josh 3:24).
The story of taking control of the land is then followed by a parallel schematic account of the allotment of the land to each of the tribes. The Transjordan (the land to the east of the Jordan River) is allotted in ch. 13; the Central regions in chs. 14—17; and then the peripheral regions to the north and south in chs. 18—19. Chapter 20 details the allocation of the five “cities of refuge”, whilst chapter 21 identifies the forty-eight towns which were allotted to the tribe of Levi, from which the priests came.

None of these are historical accounts. The schematic ordering carries symbolic weight, rather than being an historical account. Indeed, the twelve tribes of Israel were a later construction by the compiler of the narrative, rather than being an actual organisational principle at the time of any such conquest.
And even as the list of conquered peoples are identified, the savagery of this glorious moment is revealed. The memorial stones provide a reminder of the event (Josh 4:1–10), a reminder of the power of the invading force as they colonise the settled inhabitants of the land. We hear the story from the perspective of the victorious invaders—the people of Israel. The dispossession and death of so many Canaanites is simply “collateral damage” in this process.
Joshua and Israel, Britain and Australia, and the Indigenous perspective
This is a story of land, invasion, massacre, colonisation, and victory. It is an ancient story which resonates strongly with the experience of Indigenous peoples in the modern era of history. Time and time again, from late medieval times onwards, “explorers” set out from Western powers, “discovered” new lands, followed by “settlers” who came and established “civilisation”, most often by means of “subduing” the indigenous peoples, making them subservient to the “new order”—and even, in many instances, punishing those who resisted their new ways, even utilising means of killing the Indigenous peoples.
This is the dynamic of the story of “Israel entering the promised land” which is told in Joshua, as well as the story of “establishing British civilisation in the land of Australia” which is the story of the continent on which I live. It is a story of many other places, also, around t,he world today. The imposition of a new way of living by a more powerful force, the subjugation of those who already were living in the land, and the use of violence and murder to ensure that the new order was maintained and could flourish—all of this is in the history of Australia since 1788.
The story of invasion and settlement, defeat and decline, resonates with the contemporary Australian experience of the indigenous peoples of the continent and its islands. Which gives us pause for thought: how, then, do we hear and understand that story recounted in Joshua?
See also
and for my perspective on the way that biblical literalism has fed into the modern conflict over the land of Israel/Palestine, see