“When the foolish took their lamps, they took no oil with them; but the wise took flasks of oil with their lamps. As the bridegroom was delayed, all of them became drowsy and slept.” (Matt 25:3–4) These words come from the parable of Jesus which is offered by the lectionary for this coming Sunday (Matt 25:1–13). The parable serves as a warning to be ready for the arrival of the bridegroom. “Keep awake therefore, for you know neither the day nor the hour”, Jesus ends this parable (25:13).
It seems that many people in the earliest church communities expected the parousia to occur and Jesus to return from heaven into their midst at any day. Paul had indicated this some decades before this Gospel was written, telling the Corinthians that “the appointed time has grown short” (1 Cor 7:29) and “the present form of this world is passing away” (1 Cor 7:31), and warning the Thessalonians that “the day of the Lord will come like a thief in the night” (1 Thess 5:2).
Paul also describes to the Thessalonians the scene in which “the Lord himself, with a cry of command, with the archangel’s call and with the sound of God’s trumpet, will descend from heaven, and the dead in Christ will rise first; then we who are alive, who are left, will be caught up in the clouds together with them to meet the Lord in the air; and so we will be with the Lord forever”(1 Thess 4:16–17).
When writing to the Romans, Paul says that “the creation waits with eager longing for the revealing of the children of God” ahead of “the glory about to be revealed to us” (Rom 8:18–19), which again suggests an imminent occurrence; whilst the first letter attributed to Peter simply declares that “the end of all things is near” (1 Pet 4:7).
However, this much-anticipated return of Jesus to earth did not take place in the lifetime of that first generation of believers. Matthew’s Gospel, written at least four decades after the lifetime of Jesus, contains indications of how this delay impacted on people. The fact that Jesus was delayed in his appearance to his followers may have affected the faith of members of the community, or influenced others to leave the community for which Matthew was writing.
Matthew’s Jesus has in mind the coming eschatological deliverance, a deliverance which is expected imminently and that will vindicate the community as faithful and righteous to the will of God. So he tells his followers that “you will not have gone through all the towns of Israel before the Son of Man comes” (10:23). The mission that his followers undertake amongst Jews only is urgent; the end of time is coming soon, and they will not have shared “the good news [that] the kingdom of heaven has come near” (10:7) before “the Son of Man appears in heaven, and then all the tribes of the earth will mourn, and they will see ‘the Son of Man coming on the clouds of heaven’ with power and great glory” (24:30).
In this way, Matthew is typical of one type of Judaism after the destruction of the Second Temple; that of apocalyptic hope. Most of the post-70 sectarian groups express hope that God will remember his covenant with them, the faithful few of Israel, and save them; for example, 2 Baruch and 4 Ezra write that God will provide consolation for their suffering and vindicate them, whilst also punishing their enemies on the Day of Judgement (2 Baruch 6:21; 82:1–2; 4 Ezra 8:51–59; 12:34).
In these sectarian documents, the kingdom of God is eschatological is nature; it has not yet arrived on earth, though signs telling of its coming can be detected. These communities also agree that much of Israel no longer truly follows the Law of God, and that the dominant Jewish leadership is unfaithful and wicked, and that they are the ones alone representing the true Israel. Therefore, entry to the kingdom is dependent upon faithfulness to the Law as interpreted by the community.
Matthew reflects this in his reporting of words of Jesus found only in this Gospel: “do not think that I have come to abolish the law or the prophets; I have come not to abolish but to fulfill .. until heaven and earth pass away, not one letter, not one stroke of a letter, will pass from the law until all is accomplished … unless your righteousness exceeds that of the scribes and Pharisees, you will never enter the kingdom of heaven” (Matt 5:17–20). There is a fierce apocalyptic intensity behind the interpretation of Torah which the Matthean Jesus provides.

It is, however, the delay of the return of Jesus, rather than the detailed development of scenarios relating to that predicted coming, which is the issue undergirding the chapter of the Gospel that appears in our lectionary this Sunday, as well as the two following Sundays. Although the lengthy apocalyptic discourse of chapter 24 shows that Jesus appears to “buy in” to the speculative apocalyptic hypothesising of contemporary Jews, Matthew reorients this traditional material to focus on one key issue.
All three Synoptic Gospels have brought the apocalyptic discourse of Jesus to a climax with the vision, taken from Daniel 7, of “the Son of Man coming in a cloud with power and great glory” (Mark 13:26; Matt 24:30; Luke 21:27), followed soon after by the saying, “this generation will not pass away until all these things have taken place” (Mark 13:30; Matt 24:34; Luke 21:32). They each report this, surely, because Jesus believed he would be returning in glory soon after his death. Jesus was firmly grounded in the apocalyptic worldview and saw himself as the crucial prophet figure in the fulfilment of that coming end.
Mark emphasises the point with the thrice-repeated warning: “beware, keep alert, for you do not know when the time will come … keep awake … keep awake” (Mark 13:34, 35, 37). Luke likewise reports Jesus as saying “be on guard … be alert” (Luke 21:34, 36). The implication is that the return will be soon (although Luke has undertaken various editorial alterations to his sources to indicate this has not been the case).
Matthew ends the apocalyptic discourse of Jesus with a similar warning: “you also must be ready, for the Son of Man is coming at an unexpected hour” (Matt 24:44). However, he then moves immediately to report four parables, told by Jesus to remind people that they need to hold fast to their faith, be ready for whenever “the master returns”, “the bridegroom comes”, “the Son of Man comes [and] sits on his throne in glory”. In these parables, he emphasises the need to practise a sense of active waiting (24:45–25:46).
Two parables contain specific warnings about the behaviour that is expected during this period of waiting (24:45–51; 25:1–13); the second of these, which we encounter it in the lectionary this coming Sunday, is unique to Matthew. The story told in this parable indicates that active waiting involves making wise decisions, persisting tenaciously in hope for what lies in the future. The wise virgins are commended: “those who were ready went with him [the bridegroom] into the wedding banquet” (25:10). The foolish are rejected by Jesus: “truly I tell you, I do not know you” (25:12).
Similar warnings occur in other parables drawn from the Q tradition: the parable of the banquet (22:1–14), which we have read some weeks back; and the well-known parable of the talents (25:14–30), which appears next Sunday, in which the master commends his two “good and trustworthy slaves” with the words, “you have been trustworthy in a few things, I will put you in charge of many things; enter into the joy of your master” (25:21,23). By contrast, the third slave is condemned as worthless: “throw him into the outer darkness, where there will be weeping and gnashing of teeth” (25:30).
These parables all advocate active waiting as the desired form of discipleship. Being faithful to the way of Jesus means being ready for his coming, prepared for the kingdom. The message is driven home by the contrasting pairs: in this parable, wise virgins and foolish virgins; in subsequent parables, two trustworthy slaves and a worthless slave (25:14–30), and then the righteous and those who do evil (25:31–46).
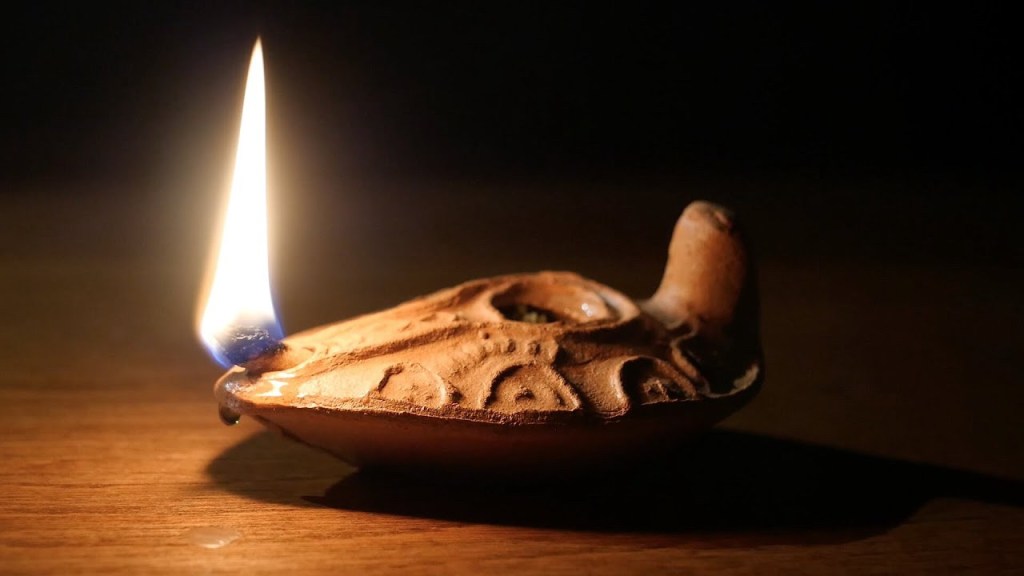

The contrast between those who are wise and those who are foolish is a trope in the Wisdom literature from which Jesus is drawing in this parable. Amongst the collected proverbs attributed to Solomon we read these aphorisms: “A wise child makes a glad father, but a foolish child is a mother’s grief” (Prov 10:1), slightly varied in “A wise child makes a glad father, but the foolish despise their mothers” (Prov 15:20), and “The wise woman builds her house, but the foolish tears it down with her own hands” (Prov 14:1).
In Ecclesiastes, the Preacher observes, “Better is a poor but wise youth than an old but foolish king, who will no longer take advice” (Eccl 4:13) and muses, “and who knows whether they will be wise or foolish?” (Eccl 2:19). The parable told by Jesus makes clear how to distinguish between the wise and the foolish: the wise are prepared, their lamps are filled with oil; the foolish had no oil.
The lack of preparedness of the five foolish bridesmaids is telling. Oil, of course, is needed to keep the lamp burning, and thus to shine light in the darkness. This basic fact lies underneath the exhortation of Jesus to his followers: “let your light shine before others, so that they may see your good works and give glory to your Father in heaven” (Matt 5:16). Well might we think that the five bridesmaids who took no oil with them were foolish! (25:1–3).
Ready access to oil in the land of Israel was secured by the blessing of God, reported in Deuteronomy: “The Lord your God will maintain the covenant loyalty that he swore to your ancestors; he will love you, bless you, and multiply you; he will bless the fruit of your womb and the fruit of your ground, your grain and your wine and your oil, the increase of your cattle and the issue of your flock, in the land that he swore to your ancestors to give you.” (Deut 7:12–13). Of course, olive trees are well suited to the Mediterranean climate, and so would have grown prolifically, ensuring a steady supply of olives for making oil, regardless of God’s covenant loyalty!
Ben Sirach affirms that “the basic necessities of human life are water and fire and iron and salt and wheat flour and milk and honey, the blood of the grape and oil and clothing” (Sir 39:26); so oil ought to have been at hand for the five foolish bridesmaids to secure.
Oil plays a key role in the religion of the Israelites. In the instructions relating to the tabernacle, Moses was instructed to “command the people of Israel to bring you pure oil of beaten olives for the lamp, that a light may be kept burning regularly” (Lev 24:1), and Aaron and his sons are delegated to ensure that it keeps burning each night as “a perpetual ordinance to be observed throughout their generations by the Israelites” (Exod 27:20–21). Oil was added to many sacrifices and offerings that were brought to the temple, as almost all of the 88 appearances of the word in Exodus, Numbers, and Leviticus attest.
Oil was also central in the ceremonies of anointing new kings—Saul (1 Sam 10:1), David (1 Sam 16;13; Ps 89:20), Solomon (1 Ki 1:39), Jehu (2 Ki 9:6), and presumably all other kings of Israel and Judah. Oil anoints the heads of faithful believers (Ps 23:5; 45:7) and “makes the face to shine” as one of the gifts provided by God to all humanity (Ps 104:15). The followers of Jesus anointed with oil those who were sick (Mark 6:13), accompanied with prayer (James 5:14); even the Good Samaritan “went to [the injured man] and bandaged his wounds, having poured oil and wine on them” (Luke 10:34).
Given its importance in Israelite culture and religion, as well as in daily life, one would have thought that the five bridesmaids would have been well prepared to meet the bridegroom, ensure their lamps were filled with oil!
Perhaps when he told this parable, Jesus also had in mind the following story involving the prophet Elisha? In this story, the wise use of oil reflects the faithfulness of a widow and her trust in the word of the prophet, which brings her an assured future. She was wise.
Now the wife of a member of the company of prophets cried to Elisha, “Your servant my husband is dead; and you know that your servant feared the LORD, but a creditor has come to take my two children as slaves.” Elisha said to her, “What shall I do for you? Tell me, what do you have in the house?” She answered, “Your servant has nothing in the house, except a jar of oil.” He said, “Go outside, borrow vessels from all your neighbors, empty vessels and not just a few. Then go in, and shut the door behind you and your children, and start pouring into all these vessels; when each is full, set it aside.” So she left him and shut the door behind her and her children; they kept bringing vessels to her, and she kept pouring. When the vessels were full, she said to her son, “Bring me another vessel.” But he said to her, “There are no more.” Then the oil stopped flowing. She came and told the man of God, and he said, “Go sell the oil and pay your debts, and you and your children can live on the rest.” (2 Ki 4:1–7)
*****
For more on apocalyptic in Israelite tradition, see
and in this section of Matthew’s book of origins, see