This coming Sunday, we will hear a story that didn’t happen—yet a story that is always happening. We hear stories from the grand saga of ancient Israel at this point in the lectionary cycle each year: stories of Abraham, Sarah, and Hagar, of Isaac and Rebekah, stories of Jacob, Leah, and Rachel, and the twelve sons of Jacob, the stories of Joseph and his brothers and the stories from early in the life of Moses.
Yet a critical approach to scripture recognises that these stories did not actually happen as they are reported; but they are told because the dynamics at work in the stories reflect the realities of life as the ancient Israelites experienced it. And we read them again, and listen, and reflect on them, because we have faith that they also convey something to us, in a very different culture and location, about the realities of life as we know it.
Personally, I don’t think we can say that these ancestral stories happened as actual historical events. Certainly, the historical elements in the story of the Exodus are impossible to validate using the standard methods of historical criticism. However, they are worth remembering and retelling, because they are always happening, in the murky depths of human life.
So this year in the cycle of the Narrative Lectionary, as we read and hear this story yet again, may it refresh our understanding of life and take us somehow into the centre of our existential being. This story and others around it have been told and retold throughout the centuries, because they express things that are deep within our lives.
The people depicted in the wilderness in today’s passage (Exodus 16:1–18) are quite relatable characters, to me. We are introduced to “the whole congregation of the Israelites” right at the start, and are told that they “complained against Moses and Aaron in the wilderness” (v.2). I’m going to pass on making any connection between this verse and any congregation of which I have been a part, or in which I have ministered. Let’s just say that humans complaining should not be a surprise to us!
However, let’s pause and consider: the complaint raised by the Israelites against Moses and Aaron appears to be quite unreasonable. How long have they been travelling in the wilderness? And already they seem to think that life was better for them back in Egypt, where “we sat by the fleshpots and ate our fill of bread”. Now, in the wilderness, the accuse their leaders of wanting “to kill this whole assembly with hunger” (v.3).
However, if you put yourself into the situation of the Israelites, you might well have a more empathic understanding of their situation. Their years in Egypt were intensely difficult: the Egyptians “set taskmasters over them to oppress them with forced labour … [they] became ruthless in imposing tasks on the Israelites, and made their lives bitter with hard service” (Exod 1:11–14). How were the Israelites to respond? Fright? Fight? or Flight??

We might hypothesise—imagining what might have been going through the minds of the Israelites in the story as they considered their situation. (As noted above, I don’t think that this was an actual historical event—but it is told in Exodus as a history-like narrative, and that history-like character invites us to consider how the hypothetical characters in that story might have thought and acted.)
In such a situation, fright would have been an understandable response. The power of the Egyptian overlords would have generated fear amongst the Israelites as they struggled to complete the increasingly demanding tasks imposed upon them. As there presumably were many years between the death of Joseph (Gen 50:26) and the time when “a new king arose over Egypt, who did not know Joseph” (Exod 1:8), that suggests that fright gripped the people and paralysed them into inaction. They continued as slaves under increasingly difficult conditions.
The thought of fight might have entered the minds of some—standing up for their rights and asserting themselves in order to gain freedom may well have been suggested, even debated, during this extended interim period. Indeed, as the story recounts, Moses himself, fuelled by a passion for justice and a dislike of injustice, was known to have intervened with passion and force into a situation of injustice—such that “he saw an Egyptian beating a Hebrew, one of his kinsfolk; he looked this way and that, and seeing no one he killed the Egyptian and hid him in the sand” (Exod 2:11–12). The next day, fearing that his actions were known, he fled across the desert to Midian, where he remained for quite some years.
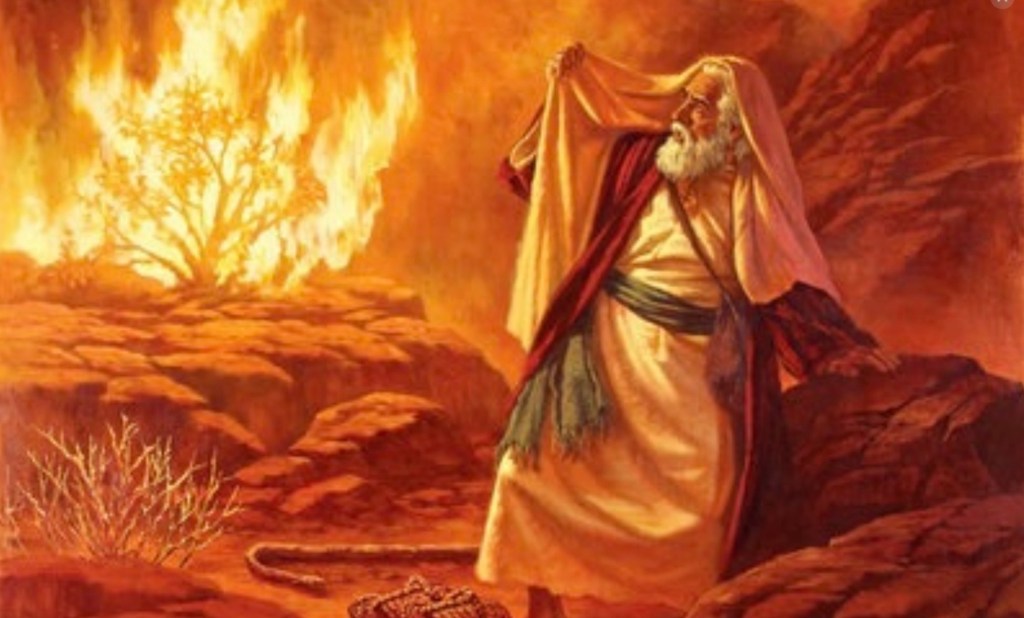
Would Moses have thought to press hard against his Egyptian overlords, agitating for them to act justly in relation to the Israelites? His initial thoughts in this regard may well have been completely deficient—that is, until he had encountered God in the burning bush (Exod 3:1–5). From that bush, the voice had come, commissioning Moses to approach Pharaoh “to bring my people, the Israelites, out of Egypt” (3:10).
Moses, of course, argued with God about what that would mean (3:11–4:17)—but in the end, he returned to Egypt (4:18–31) with the intention of confronting Pharaoh, to say “Let my people go” (5:1). The initial request was simply “so that they may celebrate a festival to me in the wilderness” (5:1)—but Pharaoh was resistant, leading to the long sequence of divinely-initiated plagues (7:14—10:28), culminating in the plague of the death of “all the firstborn in the land” (12:29–32).
It was flight, however, which won the day for the Israelites—after they, in turn, had been convinced by Moses that this was what God wanted them to do (12:3, 21–28). And that flight, according to the story line, was supported by the interventions of the divine into the sequence of human events: “at midnight the Lord struck down all the firstborn in the land of Egypt, from the firstborn of Pharaoh who sat on his throne to the firstborn of the prisoner who was in the dungeon” (12:29), and then “the Lord brought the Israelites out of the land of Egypt, company by company” (12:51), and then “the Lord went in front of them in a pillar of cloud by day, to lead them along the way, and in a pillar of fire by night, to give them light, so that they might travel by day and by night” (13:21).

Then, when confronted with the sea in front of them, “the Lord hardened the heart of Pharaoh king of Egypt and he pursued the Israelites, who were going out boldly” (14:8), and then “the Lord drove the sea back by a strong east wind all night, and turned the sea into dry land; and the waters were divided. The Israelites went into the sea on dry ground, the waters forming a wall for them on their right and on their left. The Egyptians pursued, and went into the sea after them, all of Pharaoh’s horses, chariots, and chariot drivers.” (14:21–23).
And so the story resolves the tension: “the Lord tossed the Egyptians into the sea. The waters returned and covered the chariots and the chariot drivers, the entire army of Pharaoh that had followed them into the sea; not one of them remained. But the Israelites walked on dry ground through the sea, the waters forming a wall for them on their right and on their left.” (14:27–29).
The Israelites, so the story reveals to us, had thus experienced a long sequence of frightening and troubling events—culminating in their witnessing the mass drowning of the army that was pursuing them. The narrator makes it clear that “the Lord saved Israel that day from the Egyptians; and Israel saw the Egyptians dead on the seashore” (14:30). Today, meeting people who had experienced such a sequence of events, we would recognise that they had been immersed in a series of traumas, and we would readily explain their current state of being with reference to PTSD—post-traumatic stress disorder.

Of course, as we have noted, the narrator shrugs all of this off with the glib summation, “Israel saw the great work that the Lord did against the Egyptians; so the people feared the Lord and believed in the Lord and in his servant Moses” (14:31). The narrator expects the people in the story to move on. And so we are then given the full set of lyrics of the song that Moses led the people in singing, “I will sing to the Lord, for he has triumphed gloriously … the Lord is my strength and my might … this is my God, and I will praise him” (15:1–18), followed by a recapitulation of the earlier verses in the song that Miriam and the women sang, “Sing to the Lord, for he has triumphed gloriously; horse and rider he has thrown into the sea” (15:21).
But as the story continues on, the narrator cannot but help give indication of the ways that the trauma of this long sequence of events has impacted on the Israelites. The first indication of that comes in the complaint of the people when they could find no water; they cried out to Moses, and God intervenes again to enable him to provide water for drinking (15:22–25).
There are further indications when another set of complaints is brought against Moses and Aaron, for the people are now hungry (16:1–3); then the story of another moment of complaint, at Rephidim (17:1–7); and still further stories of complaint at Num 11:1–15 and 14:1–4.
If we enter into the story and imagine the state of the people, there can be no doubt that they would have been gripped with terror and fear—wondering what the future would hold, lamenting the difficulties of the present, and looking back already on the past with “rose-coloured glasses”, unable to remember exactly how difficult and oppressive it was for them to live in Egypt.
And yet, the narrator wants us to understand that, in the midst of the complaints raised by the people, there was hope: they camped at a fertile oasis at Elim (15:27), they ate the quails and manna provided each day (16:13–18; Num 11:7–9); they had water to drink at Massah and Meribah (17:7)

The story that is shaped in the narrative of Exodus has a strong belief in an active, interventionist deity. That is possible to claim with the benefit of hindsight, knowing that the people did survive their time in the wilderness, did have nourishment and water, did eventually enter the land promised to them, and did settle and become prosperous in the land. That is the blessing of telling a story long after the time in which it is set; the long range result can be known!
It was not the case in the midst of the story, as the events being narratives took place. Doubt and fear grounded in uncertainty, as well as dysfunction generated by repeated traumatic events, would have blurred and marred any sense of confident hope, surely. And that is precisely the situation that we find ourselves in, today. Life is “happening” to us. We do not have a guarantee of the end-in-view, the longterm result that is hoped for. We live by faith, with hope, yearning and trusting.
So the story we hear this coming Sunday (Exod 16:1–18) tells of God’s provision for the people of Israel—and, by extension, for people of faith today—as they, and we, live with an attitude of hopeful expectation and patient faith.
The climax of the story, at least in terms of the verses that the lectionary offers us, is the simple affirmation that the “fine flaky substance, as fine as frost on the ground”, the “bread from heaven” that they found, was indeed “the bread that the Lord has given you to eat” (16:4, 14–15).
Later in the chapter, we are told that this was the staple diet of the people for “forty years” (16:35), which is the standard biblical expression for “a very, very long time”. And much later, of course, in Christian tradition, Jesus of Nazareth is presented as “the bread from heaven”, the “living bread” which is given “for the life of the world” (John 6:31–51)—bread which lasts, not for ”forty years”, but “forever” (John 6:51).
Also in the story told in Exodus 16, we are told that “the house of Israel called it manna” and that “it was like wafers made with honey” (16:31). An explanation of this name—drawn from the comment made in Numbers—is that the phrase means “this is aphids”, indicating that the dew was crystallised matter deposited by insects. (See “the manna was like coriander seed, and its color was like the color of gum resin”, Num 11:7.)
An alternative explanation for the name manna lies within the text of Exodus itself; for when the people ask, “what is it?” (16:15), the Hebrew is man hu. And so the name reflects the initial puzzlement—a nice ironic twist, indeed.

How do we read this story today? For me, the story of the first half of Exodus has really strong resonances with the story of millions of people in the world today. These are people that we call refugees and asylum seekers—people fleeing from oppression and mistreatment in the land where they were born, travelling through difficulties and dangers, to seek the safety of refuge in a new land; a land that becomes, for them, a land of hope, a land of promise.
The United Nations Refugee Agency, UNHCR, keeps track of current numbers and publishes a summary each year. For 2024, the figures were:

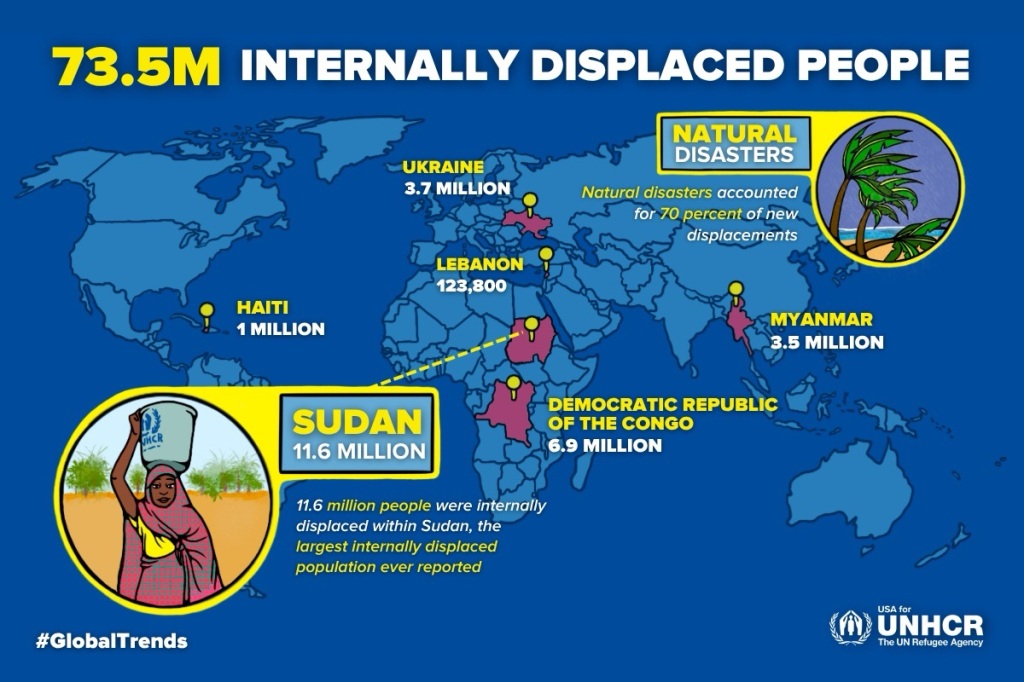
There has been a consistent rise in numbers of internally displaced people and refugees throughout this century. Compared to a decade ago, the number of refugees under UNHCR’s mandate has more than doubled. This steady increase reflects the persistence of civil war and uprisings in many places, and the impact of various natural disasters (many being the result of, or exacerbated by, climate change).
Each person in those millions of people has experienced trauma, sought to escape, travelled along difficult pathways on land or sea, and is seeking safety in another country—or is patiently waiting to be resettled from the refugee camp where they are, into another country. In their report on the situation in 2024, the UNHCR says that “While mental health issues can affect anyone, refugees and other forcibly displaced people often face additional stressors that affect their mental health. According to a survey conducted by UNHCR, refugees in all countries are at a higher risk of experiencing depression compared to the host population. Refugees who have experienced violence, are widowed or separated from their partners or who live in adverse living conditions are more likely to experience depression.”
There are other key factors noted in their report, which can be read at https://www.unrefugees.org/news/five-takeaways-from-the-2024-unhcr-global-trends-report/
Perhaps the Exodus story can resonate in our current global context, and remind us of the value of people who are seeking the safety of refuge, whether as displaced persons within their own country, or as refugees fleeing to a safe haven in another country. It can remind us of the importance of meeting the needs of these people, and the necessity of remembering the trauma that they experienced which has pushed them to flee their homeland and seek safety elsewhere.
The people of Israel, in the ancient story told by Exodus, were refugees, seeking asylum in a foreign land. And as people of faith, we might well ponder: how do we serve as the agents of God, to offer to refugees and asylum seekers, today, “the bread that the Lord has given [them] to eat”?

My take on Exodus, as not an historical account but more of a foundational myth, raises questions about preaching on such stories. I have considered this matter in this blog: